Comparison to Other Cheese Types
Cheddar cheese slice nutrition – Cheddar cheese slices are a popular choice, but how do they stack up nutritionally against other common cheese varieties? Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices about your diet. This comparison focuses on fat, protein, and key vitamin and mineral content.
Let’s delve into a detailed comparison of cheddar with mozzarella, Swiss, and provolone cheese slices, highlighting their nutritional nuances.
Nutritional Differences Between Cheese Types
The nutritional profiles of different cheese slices vary significantly due to factors like milk type, aging process, and manufacturing techniques. These differences impact their fat, protein, and vitamin/mineral content.
Understanding cheddar cheese slice nutrition is crucial for balanced eating. While cheddar offers a good source of calcium and protein, consider comparing its nutritional profile to alternatives like cottage cheese; for detailed information, check out this comprehensive guide on cottage cheese nutrition facts. Returning to cheddar, remember portion control is key to maximizing its benefits within a healthy diet.
- Fat Content: Cheddar cheese tends to be higher in fat than mozzarella, but often lower than some varieties of provolone. Swiss cheese usually falls somewhere in between.
- Protein Content: Generally, the protein content across these cheese types is fairly similar, with minor variations depending on the specific brand and production method. All are good sources of protein.
- Vitamin and Mineral Composition: While all these cheeses offer calcium, variations exist in other vitamins and minerals. For example, cheddar is often richer in vitamin A than mozzarella, while Swiss may have a higher concentration of certain B vitamins.
Comparative Nutritional Table of Cheese Slices, Cheddar cheese slice nutrition
The following table provides a general comparison. Note that specific nutritional values can vary based on brand and serving size. Always refer to the nutrition label on the specific product you are consuming.
| Cheese Type | Fat (g per slice) | Protein (g per slice) | Calcium (mg per slice) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheddar | 8-10 | 7-8 | 200-250 |
| Mozzarella | 5-7 | 6-7 | 180-220 |
| Swiss | 7-9 | 7-8 | 200-240 |
| Provolone | 9-11 | 7-9 | 220-260 |
Impact of Processing on Nutrition: Cheddar Cheese Slice Nutrition
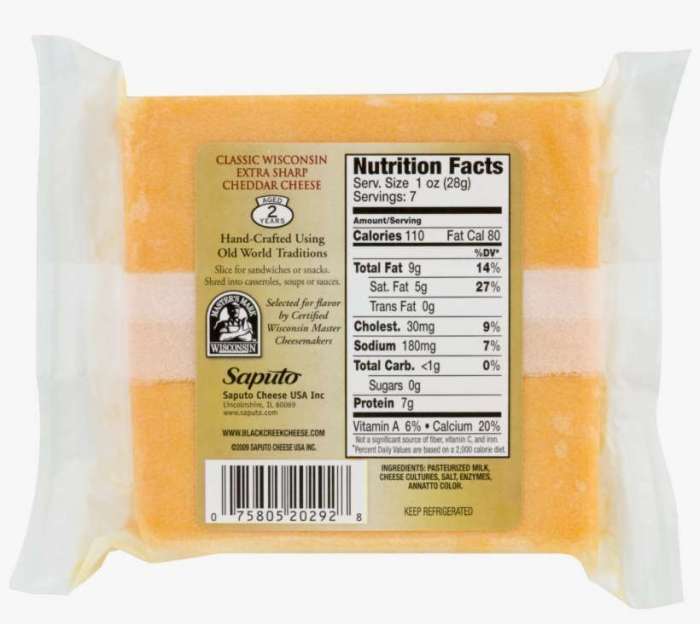

Cheddar cheese slices, a convenient and popular snack, undergo significant processing that can affect their nutritional profile compared to natural cheddar cheese. Understanding these changes is crucial for making informed dietary choices. The processes involved, from pasteurization to the addition of emulsifiers and preservatives, influence the final product’s nutritional content, sometimes leading to both losses and gains.Processing methods like pasteurization, while essential for safety, can impact the levels of certain heat-sensitive vitamins and beneficial bacteria.
The addition of ingredients such as emulsifiers and preservatives, designed to improve texture, shelf life, and prevent spoilage, also affects the overall nutritional composition. Natural cheddar, on the other hand, typically undergoes minimal processing, retaining more of its inherent nutritional value.
Pasteurization’s Effect on Vitamins
Pasteurization, a heat treatment to eliminate harmful bacteria, is a standard step in cheese production. However, high temperatures can degrade heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin B12 and certain antioxidants. The extent of vitamin loss depends on the specific pasteurization method and duration. While some nutrient loss is inevitable, pasteurization ensures food safety, a critical factor outweighing minor vitamin reductions.
For example, studies have shown that pasteurization can reduce the vitamin B12 content of milk by up to 10%, and similar effects could be observed in cheddar cheese.
Preservatives and Additives
Processed cheddar cheese slices often contain additives such as emulsifiers and preservatives to enhance texture, shelf life, and prevent spoilage. While these additives generally meet safety standards, their impact on the nutritional profile is a subject of ongoing discussion. Some emulsifiers might interfere with nutrient absorption, although research on this is still limited and requires further investigation. The addition of salt, a common preservative, should also be considered, as excessive sodium intake is linked to various health problems.
The nutritional label is key to understanding the specific additives and their quantities in a given product.
Nutritional Differences: Natural vs. Processed
Natural cheddar cheese, made with minimal processing, typically boasts a higher concentration of certain vitamins and beneficial bacteria compared to its processed counterparts. Processed cheddar slices may contain lower levels of certain vitamins due to processing and the addition of fillers. However, processed slices often have a more consistent texture and longer shelf life. The differences in nutritional value are often subtle but can accumulate over time.
Consumers can compare nutritional labels to make informed decisions based on their individual dietary needs and preferences. For example, a comparison of the vitamin B12 content per serving would highlight the differences between natural and processed cheddar.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information
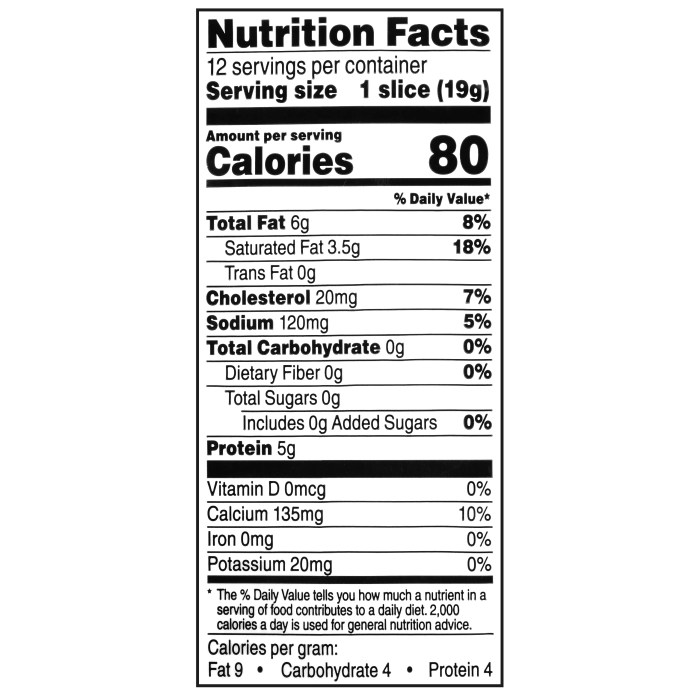
Understanding the nutritional content of a cheddar cheese slice is easier with visual aids. These representations can effectively communicate the proportions of different macronutrients and micronutrients, making it simpler to grasp the overall nutritional profile.
Imagine a circular pie chart representing a single cheddar cheese slice. The largest segment, perhaps 40%, would be a creamy yellow, representing fat. A smaller, but still significant, orange segment of around 30% would depict protein. A small, pale yellow slice, roughly 20%, represents carbohydrates. Finally, a tiny sliver, perhaps 10%, representing a mix of vitamins and minerals, could be multicolored, with small sections for calcium (light green), vitamin A (orange), and other micronutrients (a variety of small colors).
Cheddar Cheese Slice Nutritional Composition
This pie chart visually communicates the dominance of fat and protein in a cheddar cheese slice. The small carbohydrate and micronutrient sections emphasize their relatively minor contributions to the overall nutritional profile. This visual representation allows for quick understanding of the macronutrient balance, highlighting the high fat and protein content characteristic of cheddar cheese.
Comparison of Cheddar Cheese Slice with Other Foods
To further illustrate the nutritional value of a cheddar cheese slice, a bar graph comparison with other common foods is helpful. Consider a bar graph with the y-axis representing grams of protein per serving and the x-axis listing various foods. A bar representing a cheddar cheese slice would show a moderate level of protein. For comparison, a bar for a serving of chicken breast would be significantly taller, representing a higher protein content.
Conversely, a bar for a slice of bread would be much shorter, illustrating its lower protein content. Similar comparisons could be made for fat and carbohydrate content, using separate bar graphs to avoid visual clutter and maintain clarity.
FAQ Section
What are the best ways to incorporate cheddar cheese slices into a healthy diet?
Incorporate cheddar cheese slices in moderation as part of balanced meals and snacks. Pair it with fruits, vegetables, or whole grains for a more complete nutritional profile. Consider low-fat options for a reduced calorie intake.
Are there any specific health benefits associated with eating cheddar cheese?
Cheddar cheese is a good source of calcium and protein, essential for bone health and muscle building. It also contains certain vitamins like Vitamin A and Vitamin K2. However, the saturated fat content should be considered as part of an overall balanced diet.
Can cheddar cheese be part of a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Traditional cheddar cheese is not suitable for vegan diets as it is a dairy product. However, there are vegan cheddar cheese alternatives available on the market made from plant-based ingredients.
How can I store cheddar cheese slices to maintain their freshness?
Store cheddar cheese slices in an airtight container in the refrigerator to prevent spoilage and maintain quality. Proper storage can extend its shelf life significantly.




